:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/de/arteria-iliaca-externa/Zhk5nDLl5vir5BWocP5ryQ_A_iliaca_externa.png)
Ligamentum Teres Uteri Verlauf
The common iliac artery is a large artery of the abdomen paired on each side. It originates from the aortic bifurcation at the level of the 4th lumbar vertebra. It ends in front of the sacroiliac joint, one on either side, and each bifurcates into the external and internal iliac arteries . Structure
Arteria iliaca interna Medicína, nemoci, studium na 1. LF UK
The external iliac artery is the main blood supply to the lower limb as it continues down into the thigh as the femoral artery at the level of the inguinal ligament. This article will examine the anatomy of the external iliac artery, including its origins, branches and some relevant clinical information. Key facts about the external iliac artery.

Arteria iliaca communis via medici Anatomie lernen, Anatomie, Mensch körper
The common iliac artery bifurcates to give rise to the internal and external iliac arteries. The internal iliac artery supplies the pelvis, pelvic organs, reproductive organs, and the medial part of the thigh. The external iliac artery is the largest branch of the common iliac artery, and it forms the main blood supply to the lower extremity.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/de/arteria-iliaca-communis/384xAYkaUUcLHwK78oM6w_Ca4EPJ42qNOFSNQadWUcyQ_A._iliaca_communis_m01.png)
Arteria Iliaca communis Anatomie, Verlauf, Äste & pAVK Kenhub
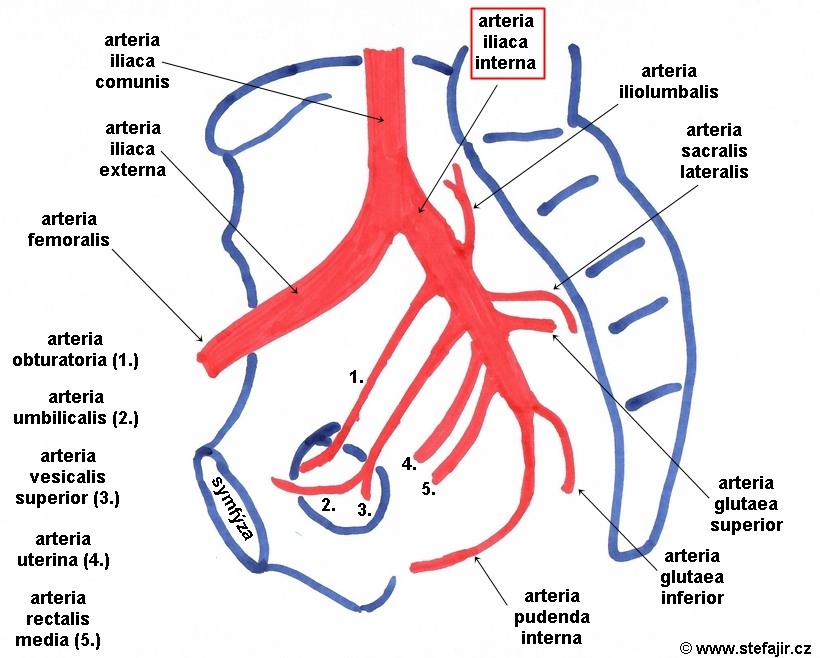
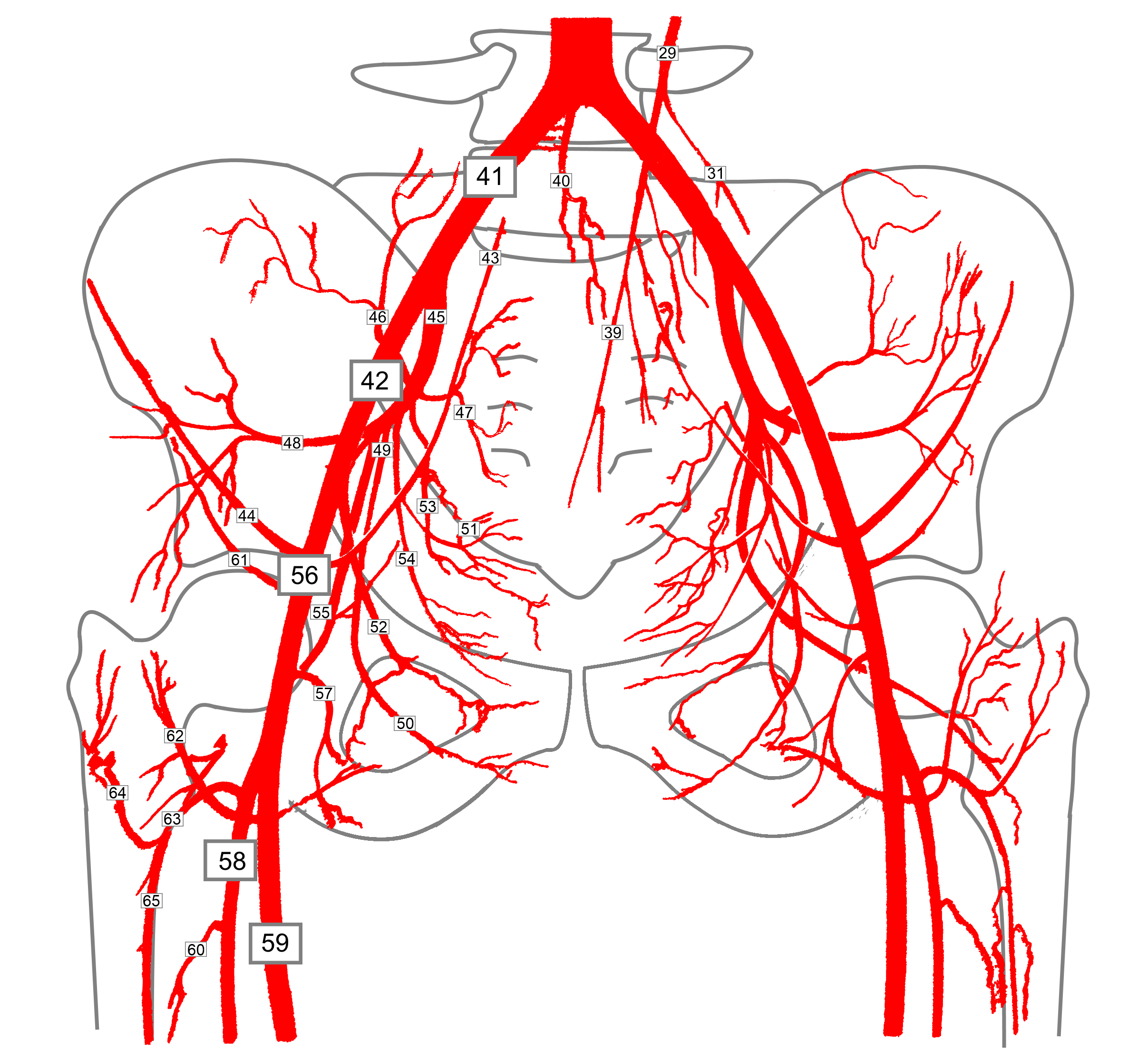
The internal iliac artery (also known as the hypogastric artery, but internal iliac is the accepted term in the TA ) is the smaller terminal branch of the common iliac artery . It supplies the pelvic walls, pelvic viscera, external genitalia, perineum, buttock and medial part of the thigh. Gross anatomy Origin
/the-blood-supply-of-the-pelvis-87376790-7b216233f31e4d5da3959a64e17e6a34.jpg)
External Iliac Artery Anatomy, Function, Significance
If there are two arteries present, one originating from the arteria iliaca interna and the other from the arteria epigastrica inferior, they should be called as the arteria obturatoria propria and arteria obturatoria acesssoria aberrans,. are termed the arteria femoralis communis* and the vena femoralis communis*.

Overview of Neurovascular Structures Basicmedical Key
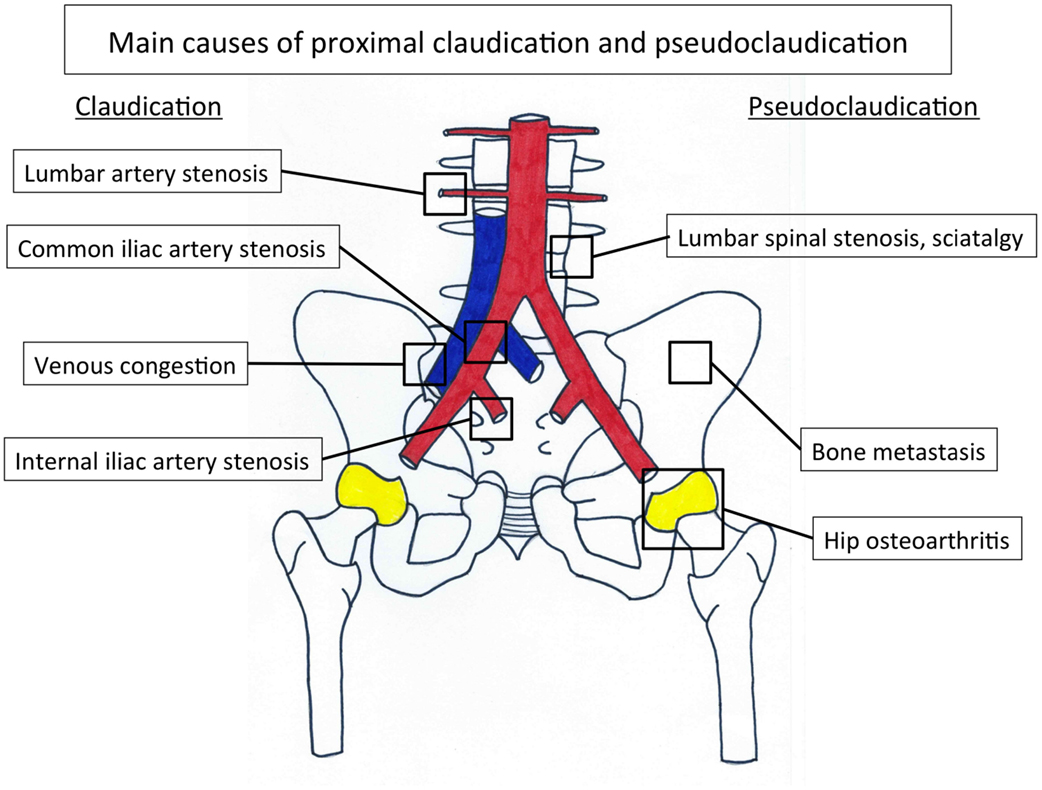
Iliac artery aneurysms (IAAs) are often diagnosed as a result of screening or other imaging studies. Symptoms do not typically occur unless the aneurysm is large and are primarily related to compression of surrounding structures. Like abdominal aortic aneurysms, IAAs have a propensity for life-threatening rupture as diameter increases.
Frontiers Internal Iliac Artery Stenosis Diagnosis and How to Manage it in 2015
The development of AAA increased with age. 24 - 26 The odds ratio for an age increase of 7 years was 1.7. 9. In conclusion, the normal reference diameter of the infrarenal abdominal aorta in the Korean population is 19.0 mm in males and 17.9 mm in females. The diameter of the abdominal aorta increases with age.

AMIGOS PARA SIEMPRE Anatomía humana Arterias
Isolated iliac artery aneurysms (IIAs) are classified according to their anatomy. The proximal non-aneurysmal artery is defined as the proximal neck or landing zone and distal non-aneurysmal artery is defined as the distal landing zone. This classification allows selection of appropriate candidates for endovascular or surgical therapy. type A

Tutorial 28 how to remember the branches of the internal iliac artery Sauropod Vertebra
Arteria iliaca communis Quick Facts Origin Course Branches Supplied Structures Quick Facts Origin: Abdominal aorta. Course: Descends in a lateral direction. Branches: Ureteric branch, internal iliac, and external iliac arteries. Supplied Structures: Pelvic cavity, perineum, and lower limbs. Complete Anatomy
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/left-common-iliac-artery-4/zbiH93jHaBoGxJXVjt3nAA_A._iliaca_communis_sinistra_02.png)
Left common iliac artery (Arteria iliaca communis sinistra) Kenhub
Common iliac artery Aortic diameter measurements Common carotid artery Cerebral arterial circle Arteries of spinal cord Subclavian artery Femoral artery Arteries Systemic veins Great lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs Nervous system Sense organs Integument Common iliac artery Arteria iliaca communis Acronym: CIA Definition
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/left-common-iliac-artery/xDjZqI0TsiquMEhyYLo5w_A._iliaca_communis_sinister_02.png)
Left common iliac artery (Arteria iliaca communis sinistra) Kenhub
The aorta is the main artery in the body whose only and important function is to carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body. It is important to note that all the arteries of the human body (except the pulmonary arteries ), no matter where they are, receive blood from the aorta.
/GettyImages-87377010-72ec77ac5a2745f086d00625d0d0d8f6.jpg)
Internal Iliac Artery Anatomy, Function, and Significance
The iliolumbar artery (which supplies blood to the abdomen) can also emerge earlier than normal at the trunk of the internal iliac artery. Function. The primary task of the common iliac artery is to deliver oxygenated blood to the pelvic area and lower limbs. Via its branches, the internal iliac artery supplies blood to the pelvic region, groin.
Surgery Assistant
In human anatomy, the iliac arteries are three arteries located in the region of the ilium in the pelvis : External iliac artery - forms where the common iliac artery bifurcates, continues as the femoral artery at the inguinal ligament. Internal iliac artery - forms where the common iliac artery bifurcates, supplies the perineum and sexual.

Pin auf Anatomy
Arteria iliaca interna 1/5 Synonyms: none The internal iliac artery begins at the common iliac bifurcation, at the level of the intervertebral disc between the L5 and S1 vertebrae. It extends for a short distance (4 cm) until the margin of the greater sciatic foramen. The internal iliac artery divides into two trunks called anterior and posterior.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1064/mAILbcS3t2vnVZMAu3OZQ_arteries-of-the-sacrum_latin.jpg)
Arteria Iliaca communis Anatomie, Verlauf, Äste & pAVK Kenhub
The common iliac arteries (CIAs) enter the pelvis on the medial aspect of the psoas muscle. The left CIA is shorter than the right. The right CIA passes anterior to the left common iliac vein and then anterior and parallel to the right common iliac vein. The left CIA course is simpler, running parallel and lateral to the left common iliac vein.

Endovaskulær behandling af mykotisk arteria iliacaaneurisme Ugeskriftet.dk
The common iliac artery (Latin: arteria iliaca communis) is a paired large elastic artery located on each side of the abdomen in the iliac region. The common iliac arteries arise from the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta, at the level of fourth lumbar vertebra (L4).